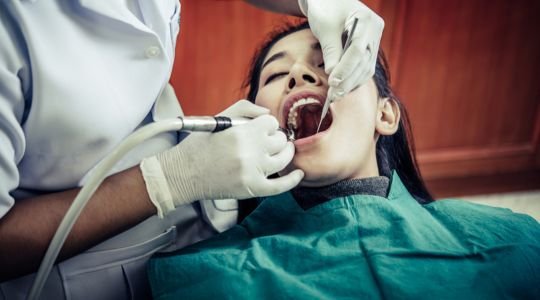
Descalling & Gum Treatment
Descaling and gum treatment are essential dental procedures aimed at maintaining oral health by preventing and treating periodontal disease, commonly known as gum disease. These procedures are typically performed by dental professionals and are integral parts of routine dental care, especially for individuals prone to plaque buildup and gum issues.
Descaling, also known as scaling, involves the removal of dental plaque and tartar (calculus) that accumulate on the teeth over time. Plaque is a soft, sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth and gums after eating or drinking. If not removed through regular brushing and flossing, it hardens into tartar, which cannot be removed by brushing alone. Descaling is usually done using specialized dental instruments such as ultrasonic scalers and manual hand scalers. Ultrasonic scalers use high-frequency vibrations to break up plaque and tartar, which are then washed away with a stream of water. Manual hand scalers are used to scrape off the remaining deposits, especially in hard-to-reach areas.
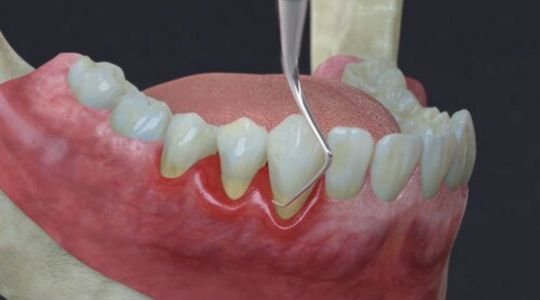
Gum treatment, often referred to as periodontal therapy, involves a range of procedures designed to treat and prevent gum disease. The early stage of gum disease, known as gingivitis, is characterized by red, swollen gums that may bleed easily. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease that can lead to tooth loss and damage to the bone supporting the teeth. Gum treatment may include deep cleaning procedures such as root planing, where the surfaces of the tooth roots are smoothed to remove bacteria and tartar from deep periodontal pockets and to discourage further buildup. In more advanced cases, surgical procedures such as flap surgery, bone grafts, and tissue grafts may be necessary to restore gum health and structure.
Regular descaling and gum treatment are crucial for preventing periodontal disease and maintaining overall oral health. These procedures help to remove the bacteria and toxins that cause inflammation and infection in the gums, thereby preventing the progression of gum disease. Additionally, maintaining good oral hygiene practices at home, such as brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, and using an antiseptic mouthwash, can significantly reduce the risk of gum disease and the need for extensive dental treatments.
Descaling and gum treatment are vital dental procedures that play a key role in preserving oral health by addressing plaque buildup and gum disease. Regular visits to the dentist for these treatments, combined with good oral hygiene habits, can ensure healthy teeth and gums for a lifetime.
What is the best treatment for gum disease?
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common condition that affects the tissues surrounding the teeth. The best treatment for gum disease varies depending on the severity and progression of the condition, ranging from non-surgical therapies to more advanced surgical interventions.
In the early stages, known as gingivitis, the best treatment typically involves professional dental cleaning combined with improved oral hygiene practices. This includes brushing at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, and using an antiseptic mouthwash to reduce plaque and bacteria. Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are crucial to prevent the progression of gingivitis to more severe forms of gum disease.
For more advanced stages, known as periodontitis, the treatment becomes more intensive. Scaling and root planing, a deep-cleaning procedure that removes plaque and tartar from below the gumline and smooths the root surfaces, is often the first line of defense. This helps to eliminate bacteria and promote healing of the gum tissue.
In cases where non-surgical treatments are not sufficient, surgical options may be necessary. These can include flap surgery, where the gums are lifted back to remove tartar deposits and then sutured back in place, and bone grafting, which aims to regenerate lost bone and tissue supporting the teeth. Guided tissue regeneration and soft tissue grafts may also be used to restore damaged areas.
Additionally, adjunctive therapies like antibiotic treatments (both topical and systemic) may be prescribed to target persistent bacterial infections. Laser therapy is another emerging treatment that can effectively reduce bacteria and promote the reattachment of gums to teeth.
Ultimately, the best treatment for gum disease involves a combination of professional dental care and rigorous personal oral hygiene. Early detection and proactive management are key to preventing severe complications, such as tooth loss and systemic health issues linked to periodontal disease. Regular dental visits and maintaining a proper oral hygiene regimen are essential components of effective gum disease treatment and overall oral health.



